
New clients, unlock 10% off all plans 🔥 at checkout with code: CEO10SPECIAL (Limited Time Offer)
New clients, unlock 10% off all plans 🔥 at checkout with code: CEO10SPECIAL (Limited Time Offer)






Leadership is a critical skill in all areas of life, from business to politics, from sports to education.
A good leader can inspire, motivate, and guide a group of people towards a common goal, while a bad leader can demotivate, frustrate, and even harm their followers.
Thus, mastering the art of leadership is an essential step for anyone who wants to make a positive impact on the world and achieve their personal and professional goals.
However, leadership is not a one-size-fits-all concept, and there are different levels of leadership that correspond to different stages of personal and organizational development.
In this article, we will explore the 5 levels of leadership framework developed by John C. Maxwell, a renowned author, speaker, and leadership expert.
According to Maxwell, each level builds on the previous one, and the highest level represents the pinnacle of leadership excellence.
Whether you are a seasoned CEO or a budding entrepreneur, a team captain or a community volunteer, understanding these 5 levels of leadership can help you assess your current level, identify your strengths and weaknesses, and chart a path towards continuous improvement.
So, let’s dive into the world of leadership and explore the 5 levels of leadership today.
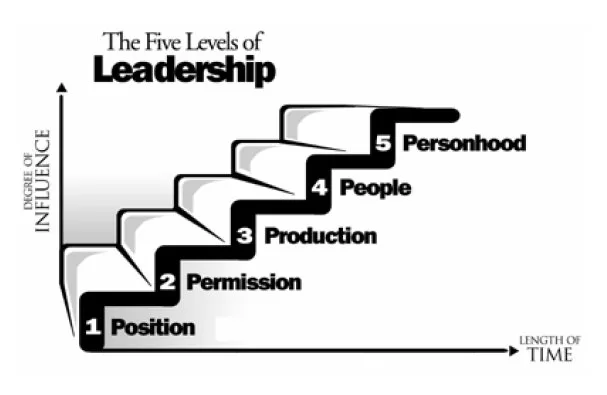
Position Leadership is the first level of leadership in John C. Maxwell’s 5 Levels of Leadership.
At this level, leaders are given their position or title by virtue of their role or job, rather than by their personal qualities or accomplishments.
Position Leadership is characterized by a focus on authority and power, and the leader’s ability to give orders and enforce compliance.
This type of leadership is often associated with traditional hierarchical structures, where the leader is at the top of the pyramid and has a clear chain of command.
Position Leaders are defined by their formal authority and control over others. They rely on their title, position, or job description to establish their legitimacy and influence.
Some of the key characteristics of Position Leaders include:
Power-based authority
Position Leaders derive their authority from their position or title, rather than from their personal qualities or accomplishments. They may use their power to make decisions, set goals, and enforce rules.
Top-down communication
Position Leaders tend to communicate in a one-way, top-down manner, where they give orders and expect compliance. They may not listen or take feedback from their subordinates.
Limited influence
Position Leaders’ influence is limited to their formal role or job description. They may not have the trust or respect of their followers, and may struggle to motivate or inspire them.
Narrow perspective
Position Leaders may have a narrow perspective on the organization and its goals, focusing only on their own department or function. They may not see the big picture or the long-term implications of their decisions.
Position Leaders can be found in all types of organizations, from the military to the corporate world.
Here are some examples of Position Leaders:
Military officers
Military officers are often Position Leaders, who are given their rank and authority by the organization. These individuals are responsible for commanding their troops and executing their missions.
Corporate executives
Corporate executives, such as CEOs, are also Position Leaders, who are appointed by the board of directors. They set the company’s strategy and direction, and ensure its financial performance.
Government officials
Government officials, such as elected officials or civil servants, are also Position Leaders, who are given their authority by the state. They are responsible for implementing policies and delivering services to the public.
While Position Leadership can be effective in certain situations, it also has its limitations. Some of the main drawbacks of Position Leadership include:
Lack of trust
Position Leaders may struggle to gain the trust and respect of their followers, especially if they rely solely on their formal authority.
Without trust, it is difficult to build strong relationships and achieve high levels of performance.
Limited creativity
Position Leaders may be more focused on maintaining the status quo and following established procedures, rather than taking risks or experimenting with new ideas.
This can lead to a lack of innovation and creativity in the organization.
Resistance to change
Position Leaders may resist change, since it can threaten their authority and power.
They may be more inclined to maintain the existing structures and processes, even if they are no longer effective.
Find out: The Predictive Index Test: Full Guide

Permission Leadership is the second level of leadership, and it builds on the foundation of Position Leadership.
While Position Leadership is based on the authority of the leader’s title or position, Permission Leadership is about earning the trust and respect of others, and creating a positive environment where people feel comfortable expressing themselves and contributing to the group.
Permission Leaders focus on relationships and communication, and they use their emotional intelligence and empathy to connect with people on a personal level.
They listen actively, ask questions, and provide support and feedback that helps others grow and develop.
They create a positive environment
Permission Leaders create a culture of trust, respect, and collaboration, where people feel safe to express their ideas and opinions, and where mistakes are viewed as opportunities to learn and improve.
They communicate effectively
Permission Leaders are skilled communicators who can convey their ideas clearly and persuasively, and who can listen actively and empathetically to others.
They build relationships
Permission Leaders focus on building strong, positive relationships with their followers, and they work hard to earn their trust and respect.
They empower others
Permission Leaders give their followers the autonomy and support they need to take risks, make decisions, and contribute to the group’s success.
Oprah Winfrey
As a talk show host, media mogul, and philanthropist, Oprah Winfrey has built a reputation for being a compassionate and empathetic leader who connects with people on a personal level.
She is known for her ability to listen to her guests and viewers, and to provide them with the support and encouragement they need to overcome their challenges.
Tony Hsieh
As the former CEO of Zappos, Tony Hsieh was known for creating a positive and supportive company culture that focused on building relationships with employees and customers.
He believed that by treating people well and creating a happy workplace, he could drive success and profitability.
Permission Leadership builds on the foundation of Position Leadership by recognizing that titles and positions alone are not enough to inspire people to follow a leader.
Permission Leaders understand that they must earn the trust and respect of their followers by creating a positive and supportive environment, and by empowering others to contribute to the group’s success.
Through focusing on relationships, communication, and empowerment, Permission Leaders can inspire their followers to be more engaged, committed, and productive.
They can create a culture of innovation, creativity, and collaboration, where everyone feels valued and supported.
Permission Leadership is a critical level of leadership that enables leaders to build strong relationships with their followers and create a positive and supportive work environment.
Find out: 50+ Best Inspirational Career Quotes for Your Career

Production leadership is the third level of leadership, and it is all about getting results.
At this level, leaders focus on achieving measurable outcomes and meeting targets. They are more results-oriented than relationship-oriented, and they tend to be good at setting goals and holding people accountable for achieving them.
Results-oriented
Production leaders are focused on achieving results and meeting targets. They are driven by the desire to produce and deliver tangible outcomes.
Goal-oriented
Production leaders set specific, measurable, and achievable goals that align with their organization’s mission and vision.
Accountable
Production leaders hold themselves and their team members accountable for meeting their goals and achieving the desired results.
Performance-driven
Production leaders measure success based on performance and productivity, and they constantly strive to improve both.
Task-oriented
Production leaders are more concerned with task completion than building relationships, although they understand that strong relationships are important for achieving results.
Find out: 10 Proven Career Advancement Strategies
Steve Jobs
As the CEO of Apple, Steve Jobs was a master of production leadership.
He was relentless in his pursuit of delivering innovative and high-quality products that met the needs and desires of his customers.
Jack Welch
As the former CEO of General Electric, Jack Welch was known for his results-driven approach to leadership.
He focused on achieving measurable outcomes and holding his team members accountable for meeting their targets.
Mary Barra
As the CEO of General Motors, Mary Barra has a reputation for being a production-oriented leader. She has been praised for her focus on quality, efficiency, and profitability.
Production leadership builds on the foundation of Permission leadership, which is all about building relationships and creating a positive work environment.
In order to achieve results, Production leaders need to have the trust and buy-in of their team members.
Permission leadership provides the necessary foundation for Production leaders to establish this trust and create a culture of accountability and high performance.
While Production leadership is vital for achieving results, it can also have some limitations.
Leaders who are too focused on production may neglect the needs and concerns of their team members, which can lead to low morale and high turnover.
Additionally, leaders who are solely focused on achieving results may sacrifice quality or ethical standards in order to meet their targets.
In summary, Production Leadership is a critical level of leadership that focuses on achieving measurable outcomes and meeting targets.
While it builds on the foundation of Permission leadership, it also has its own limitations and challenges.
A good leader must be able to balance the need for results with the need for building strong relationships and maintaining high ethical standards.
Find out: These 14 Leadership Traits Can Fuel Your Career Success
People Development Leadership is all about developing the potential of others.
People Development Leaders focus on building a team of capable and confident individuals who can take on bigger and more challenging roles.
These leaders recognize that the success of the team depends on the development of each team member, and they take an active role in helping them grow.
They have a growth mindset
People Development Leaders believe that everyone has the potential to grow and develop, and they actively seek out opportunities to help their team members do so.
They are great communicators
People Development Leaders are skilled at giving feedback, coaching, and mentoring their team members.
They are able to communicate their expectations clearly and provide constructive criticism when needed.
They empower their team
People Development Leaders give their team members autonomy and trust them to make decisions.
They create a safe and supportive environment where team members feel empowered to take risks and learn from their mistakes.
They are good listeners
People Development Leaders take the time to listen to their team members’ ideas and concerns. They value their team members’ opinions and use their feedback to improve their leadership style.
Bill Gates
Gates is known for his focus on developing the potential of others. He has invested heavily in education and has created several programs aimed at helping students and teachers improve their skills.
Oprah Winfrey
Winfrey is a master of people development. She has launched several successful careers and has mentored countless individuals over the years.
Tony Robbins
Robbins is a motivational speaker and coach who has helped thousands of people reach their full potential. He is known for his focus on personal growth and development.
Production leaders are focused on achieving results and driving performance.
People Development Leaders take this a step further by recognizing that the success of the team is directly tied to the development of each team member.
Through investing in their team members’ growth and development, they are able to create a high-performing team that can achieve even greater results.
Find out: The Best Books for Professional Development and Success

Pinnacle leadership, also known as People Pinnacle Leadership, is the highest level of leadership according to John C. Maxwell’s 5 Levels of Leadership.
This level of leadership is marked by a rare combination of humility and fierce resolve, which allows Level 5 leaders to inspire their teams to achieve extraordinary results.
Humility
Pinnacle leaders are humble and modest, and they don’t seek personal glory or attention. They give credit to others for their success and take responsibility for their failures.
Strong Will
Pinnacle leaders have a strong will to succeed, but their ambition is directed towards the organization’s success rather than their own personal gain.
Empathy
Pinnacle leaders have a deep understanding and compassion for others, and they prioritize the needs of their team members over their own interests.
Strategic Vision
Pinnacle leaders have a clear and compelling vision for the organization’s future, and they develop long-term strategies that align with that vision.
Commitment to Excellence
Pinnacle leaders have a relentless pursuit of excellence, and they hold themselves and their team members to the highest standards of performance and conduct.
Mother Teresa
Mother Teresa was a Catholic nun who dedicated her life to serving the poor and sick in India.
She embodied Pinnacle leadership through her humility, empathy, and commitment to serving others.
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States and is widely regarded as one of the country’s greatest leaders.
He demonstrated Pinnacle leadership through his humility, strong will, and strategic vision for the nation.
Alan Mulally
Alan Mulally was the CEO of Ford Motor Company from 2006 to 2014. He is credited with turning around the struggling company by implementing a clear and compelling vision, fostering a culture of teamwork, and prioritizing the needs of customers and employees.
Pinnacle leadership builds on the foundation of People Development leadership by taking the focus off the leader’s own success and putting it on the success of the organization and its people.
Pinnacle leaders understand that their legacy will be measured by the impact they have on others, and they prioritize the development and well-being of their team members over their own personal advancement.
Level 5 leadership is the pinnacle of leadership and represents the ultimate goal of any leader.
While it takes time and effort to develop the skills and qualities of a Pinnacle leader, the benefits are significant.
John Maxwell said, “The pessimist complains about the wind. The optimist expects it to change. The leader adjusts the sails.”
Mastering the art of leadership requires understanding and implementing the five levels of leadership.
Each level builds upon the previous one and involves different skills and behaviors that are essential for effective leadership.
Level 1 is about using positional power, while Level 2 is about building relationships and earning permission to lead.
Level 3 focuses on achieving results and Level 4 is about developing people. Finally, Level 5 is the pinnacle of leadership, where leaders create lasting impact and leave a legacy.
It’s vital to note that leadership is a journey, not a destination. Effective leaders are always looking for ways to improve their skills, knowledge, and abilities.
Whether you’re a seasoned executive or just starting your career, developing your leadership skills is essential for success in any field.
If you’re looking to take your career to the next level, consider investing in yourself and your future by working with a professional resume writing service like CEOMichaelHR.
With our affordable rates and expert guidance, we can help you craft a compelling and effective resume that showcases your skills, accomplishments, and potential as a leader.
So don’t wait any longer- start mastering the art of leadership today and let CEOMichaelHR help you take your career to new heights!
Share
Further Reading
*The names and logos of the companies referred to in this page are all trademarks of their respective holders. Unless specifically stated otherwise, such references are not intended to imply any affiliation or association with CEOMichaelHR.
Land interviews 3x faster while submitting fewer resumes
Copyright © 2026, ceomichaelhr.com.
All rights reserved.
Land interviews 3x faster while submitting fewer resumes
Copyright © 2026, ceomichaelhr.com.
All rights reserved.

Learn the same techniques our expert resume writers have used to get thousands of clients closer to their next job
Unlock expert resume tips, start landing multiple interviews!

Stay connected to receive powerful career insights, updates, and inspiration that’ll help you hit your career goals.